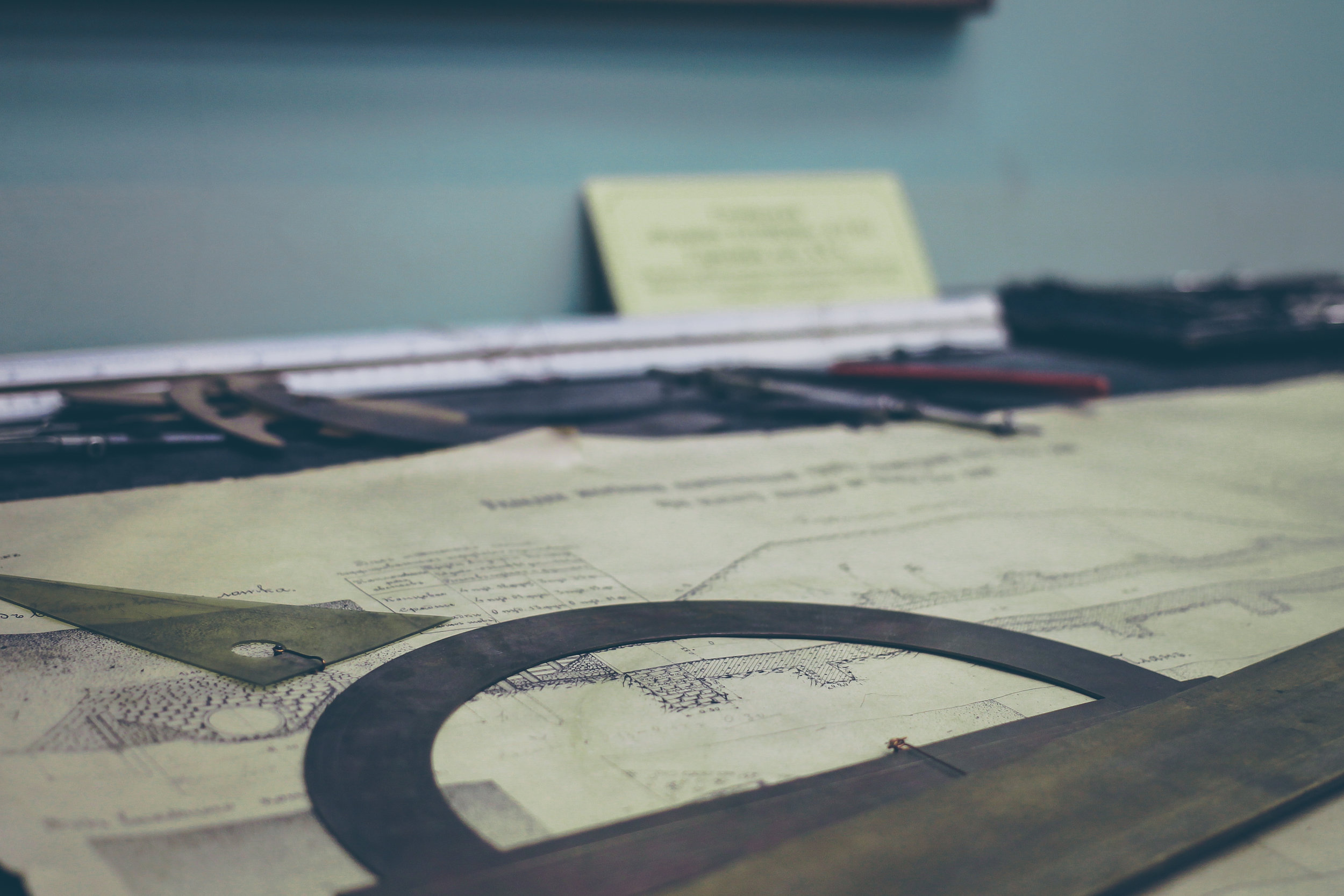
HVAC engineers are the ones responsible for the design, installation and maintenance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning - HVAC systems. As per client needs, an HVAC engineer will design and size a suitable system that fits the architectural model of an AEC project. This point on, an engineer may be involved in one or more of the following tasks:
Heat Load Analysis of a project
Preparation of conceptual model
Preparation of detailed design
Installation of HVAC system
Analysis of an installed system
Regular maintenance supervision of HVAC systems
Repair and fault analysis of existing systems
The actual nature of the job ultimately depends on whether you work for a consultancy (design), inspection agency(analysis), or an hvac contractor (construction).
What is hvac?
HVAC refers to the set of systems in a building responsible for the distribution of fresh and conditioned air.
Typical days as an engineer
1. Consultancy
At a design firm, an HVAC engineer will be expected to come in and analyse architectural designs of buildings. Based on this analysis, you will have to carry out heat load calculations which are mostly computerized these days. Once this is done, you will design the layouts of the HVAC systems that are to go in the building with the help of drafting and modelling tools like AutoCAD, Revit, Creo, etc.
Additionally, you may be asked to carry out site visits and quality checks to ensure that construction takes place in accordance with design. Depending on the role you play in the organization, these activities may also involve having to deal with clients in order to understand their requirements and collaborating with fellow engineers and architects.
2. Contractor
When working with a contracting company you will be responsible for ensuring proper installation of HVAC services in a project. You may be tasked with preparation of procurement schedules, preparation of inspection documents, preparation of testing documents, supervision of installation, commissioning, and maintenance activities, etc.
On site you will have to ensure necessary approvals for all drawings. You will have to inspect and confirm that all machines, ducts, pipes, accessories, etc. are available and approved before commencement of installation procedures. You will have to coordinate with other disciplines for installation of HVAC services without clashes. Site engineers will also be tasked with ensuring that personnel working under them are properly trained and in possession of the right equipment. You will also be a part of regular meetings with the management and quality assurance departments.
3. Inspection Agency
When working with an inspection agency, your primary task will involve the analysis of installation and construction activities on site. You will have to conduct assessments of materials, equipment, installations, and check whether they conform to approved design drawings, regulations and building codes. You will have to check if the contractor is following standards and safety procedures and report non-conformance if applicable.
Significance in the life-cycle of a building
An AEC project requires the coordinated efforts of a multitude of people from various disciplines. Architects, firefighting system designers, electrical engineers, structural engineers, and HVAC engineers work together with other consultants to achieve the desired result for the client. A well functioning HVAC system is critical in ensuring occupant comfort and health. Moreover, the HVAC system is also responsible for a major share of the building’s energy use. This necessitates the importance of proper design and installation of HVAC services.
Challenges
HVAC engineers, like anybody involved in the construction industry will be tasked with being a part of highly complex teams performing diverse processes. The nature of the profile will involve communication and coordination with other branches of the vine. Managements are ever under pressure to reduce costs owing to the highly competitive nature of the field and this trickles down to the engineers who have to ensure that savings do not come at the cost of quality or safety. System installation and maintenance also has to be handled with care as any downtime in the HVAC system will be dealt with severe criticism as no client will be polite or reasonable once their comfort is compromised. Another point to note is the presence of extreme climatic conditions at construction sites although how much this affects you will ultimately depend on your position in the firm. All of this coupled with strict deadlines can prove to be especially tricky.
Educational requirements
HVAC engineers are primarily from the mechanical discipline. A candidate looking towards a career in this industry will need to possess at least a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering. You can also choose to go for a master’s degree in HVAC. As you progress in your career, you can get certified in various sub-disciplines like energy modelling, energy assessment, high performance building design, healthcare facility design, and building operations. Industrial MEP courses are also available in the market which train novices in all hvac basics like hvac duct design, pipe design, estimation and other fundamental practices.
Other characteristics expected of a quality HVAC engineer are:
Communication skills
Mathematical ability
Logical reasoning
Problem solving skills
End word- As a career choice
A career in the HVAC industry can be a highly rewarding experience. The industry is to set to surge in productivity with breakthroughs in design and manufacturing technologies. Use of artificial intelligence algorithms in design, and automation in construction practices by hvac companies will open up fresh avenues for career choices. Employment options are well paid with plenty of scope for climbing up the corporate ladder. This is an industry where the fundamentals remain unchanged and ergo quality engineers with relevant experience are always in high demand. The same goes for technicians in the field as well. Skilled HVAC technicians consistently warrant the highest pay rates.
As living standards improve, a greater part of the world population will move to modern living quarters. This translates to increased demand for air conditioners and associated projects, which will ultimately lead to increased demand for novel structures and resourceful AEC projects.
Recent global average temperatures have soared at alarming rates decade over decade. The effects of climate change are starting to show with variations in weather patterns changing world over. In such a climate (pun intended) there will be a sharp increase in the need for efficient, cost-effective HVAC systems. Whether or not humanity is able to reverse global warming, hitching your career onto the HVAC wagon seems like nothing but a clever choice.